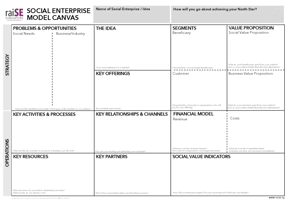
The Social Enterprise Model Canvas (SEMC) provides a strategic framework that outlines the key...
RIC06 Developing Your Social Enterprise Model Canvas
Previously we introduced the Social Enterprise Model Canvas, its function, foundations and components of strategic and operational planning. (Read more: Where to begin? The Social Enterprise Model Canvas)
Now we will explore more about how to begin developing your own Social Enterprise model canvas and the individual areas within the strategic and operational components
The SEMC Strategic Component
Identify Your Problems and Opportunities
Like any business, Social Enterprises begin by identifying and defining key problems, opportunities, and emerging trends within the social and business landscape.
Evidence-Based Framing of the Opportunity
When filling in this section, consider the specific problem or opportunity you aim to address. Support your framing with relevant data and evidence to strengthen your problem and opportunity statements.
Future-Oriented Thinking
Refine your idea by questioning whether the identified problem or opportunity is significant, scalable, and presents a viable pathway for your Social Enterprise to grow.
Create the Big Idea
The big idea serves as the foundation of your business concept, defining what your enterprise will do. This is your opportunity to creatively design a solution through your product or service.
Identify Your Differentiation
Explore the current landscape. Are there existing businesses addressing the same problem? If so, consider how your solution will stand out and provide a distinct approach to solving the issue.
Plan Ahead
Develop a future-oriented big idea that aligns with industry shifts, trends, gaps, and technological developments. Leverage these changes to create an innovative and sustainable business solution.
Define Your Key Offerings
For a business to effectively address a problem, it must deliver key offerings to its users or beneficiaries.
Focus on Unaddressed Needs
While designing key offerings, go beyond the obvious. Identify and bridge unresolved or under-addressed needs that your target audience faces.
Look Beyond Functionality
Successful offerings consider not only functional utility but also emotional and social factors. By addressing these aspects, you can foster customer loyalty and ensure a positive user experience.
Incorporate Social Good
Social Enterprises must integrate social impact into their business models. Consider how your unique solution embeds positive change at its core.
Identify Your Segments (Market and Social Segments)
Social Enterprises cater to multiple segments. You can break them down into three categories:
- Target Beneficiaries – Individuals experiencing deprivation that your Social Enterprise aims to address.
- Target Customers – Individuals who pay for your product or service.
- Target Users – Individuals who use the product or service, though they may not be the paying customers.
In some cases, target beneficiaries may be distinct from customers and users. However, in other instances, they may overlap.
Example:
A Social Enterprise provides STEM education programs for children at a subsidized rate for low-income families.
- Target Beneficiaries: Children from low-income families.
- Target Customers: Parents paying for the program.
- Target Users: The children participating in the program.
Address Latent Problems
While identifying target segments, ensure that you understand their core issues. Investigate why their needs remain underserved and how your key offerings present a solution.
Craft Your Social Enterprise’s Unique Value Proposition
A value proposition defines the tangible benefits your customers and beneficiaries receive from your product or service. It helps sharpen your competitive advantage, focus your operations, and attract potential partners.
Focus on Pain Points and Marketability
Your value proposition should address the most critical pain points faced by your target customers and beneficiaries. Pair these insights with an understanding of what customers are willing to pay for to ensure long-term sustainability.
Define the Value Being Created
Clearly articulate the benefits your target segments will gain from your offering. This distinction will help differentiate your enterprise from existing solutions in the market.
Ensure Uniqueness
A strong value proposition should be difficult to replicate. Ask yourself: What makes your approach unique, and how does it stand apart from competitors?
Develop Your Business and Social Value Proposition Statements
Use the following template to craft a compelling business and social value proposition:
My Business Value Proposition:
__________________ (Social Enterprise name) is designed
for__________________ (target Beneficiary)
who __________________ (problem or opportunity).
we will __________________ (unique product/service)
in order to __________________ (deliver outcome)
My Social Value Proposition:
__________________ (Social Enterprise name) is designed
for__________________ (target customers / users)
who __________________ (problem or opportunity).
we will __________________ (unique business intervention)
in order to __________________ (deliver desired social impact)
By leveraging these tools and guidelines, you will be able to articulate the uniqueness of your Social Enterprise’s idea, ensuring both business success and meaningful social impact.
The SEMC Operational Component
Once your strategy has been defined and the objectives have been set, it is time to think through how it would be operationalised through the business. Identifying these individual operational areas will test the feasibility and viability of your Social Enterprise.
Identify the key activities and processes needed to make the idea work
In order to make an idea work, key activities and processes have to be in place to set the conditions for success. These may include design and research, order fulfillment, delivery system implementation and outreach activities. Explore as many that you require in order to ensure the successful planning of your business activities.
List down the key channels used to reach the segments identified in the SEMC’s strategic component
Customers do not miraculously appear for our businesses. Businesses need to know how they would reach them. Some things you can explore is how you will reach your customers, and what needs to happen for your customers, beneficiaries or users to experience your offering seamlessly.
Explore alternatives to direct channels.
Some interactions with customers may be directly through the business. However there are other methods of reaching customers that may not require you to engage them directly. Some things to consider are:
- Distribution approach: Will your channels be direct (selling to the customers yourself) indirect (through partners) or automated (through self-service platforms)?
- Medium of delivery: Will your offering be delivered physically (e.g. retail, or events) or digitally (e.g. online platforms, or apps)
- Your business model: Will you operate as
- B2C (Business-to-Consumer) Selling directly to individual customers
- B2B (business-to-Business) Providing products/services to other businesses
- B2B2C (Business-to-Business-to-Consumer) Partnering with businesses to reach end consumers.
Choosing the right channels is essential for ensuring your social enterprise reaches the right audiences effectively. By strategically selecting and integrating these channels, you can maximise your impact, enhance accessibility and build a sustainable model for delivering your solution.
Define the key resources required
Assess the essential resources needed to deliver your product or service to users, customers, and beneficiaries. These resources may be physical, intellectual, human, technological, or financial.
Resources could include:
- Critical knowledge, expertise, and assets fundamental to business operations
- Core operational requirements and social impact activities integrated into the business
- Supplementary resources available through partnerships (see the next section for more information on key partners)
Understanding exactly what your Social Enterprise needs to operate is crucial for long-term success and identifying operational gaps that could affect sustainability.
Identify the key partners needed
Partners are individuals or businesses essential to making your business happen. These partners are integral to the Social Enterprise, providing opportunities, resources, and support needed for success.
Business Partners
Business partnerships form strategic relationships required for market entry, product development, technology advancement, product placement, visibility, and accessing accreditation and funding opportunities.
Building relationships with these partners is crucial for supporting your Social Enterprise's operations and activities.
Social partners
For Social Enterprises, maintaining a network of social partners is essential to deliver core social impact. These include social service organizations that collaborate on community outreach, beneficiary engagement, and impact validation.
Creating meaningful value for these partners and their beneficiaries helps ensure sustainable value creation for the Social Enterprise.
Design a financial model for business sustainability
A key challenge for Social Enterprises is generating sufficient revenue to sustain social impact while maintaining business operations. Two crucial elements to consider are revenue streams and cost structure.
Revenue Streams
Social Enterprises need diverse revenue streams to achieve financial viability. Recurring revenue is essential to finance ongoing operations and enable the scaling of social impact.
Revenue can come from multiple sources, including retail sales, training programs, consultancy work, professional services, subscription models, and service packages.
Cost Structure
Developing a cost structure requires careful consideration of major expenses. This includes analyzing both fixed and variable costs while managing capital expenditure (Capex) effectively.
Consider ways to make your cost structure efficient and adaptable. This might involve strategic decisions about resources and assets—whether to manufacture, purchase at lower costs, rent, or share them to maintain cost flexibility.
Social Impact measures
At the core of a Social Enterprise is its social impact. It guides the why of the business and helps the Social Enterprise measure the success of their social impact activities,
A development of a Social Enterprise and its social impact model begins with the “Theory of Change” where you would define the desired social change that the Social Enterprise is seeking to make. This would enable the Social Enterprise to map out the necessary resources, activities, interventions and indicators needed to achieve the measurable social impact.
Continue your raiSE Impact Community Journey
If you are part of the raiSE Impact Community, we have designed a 7-step journey that would guide you towards strategic incorporation of social impact in your business.
-
- 01 Starting your Impact Journey
- 02 What is a raiSE Social Enterprise?
- 03 The raiSE Ecosystem
- 04 How a Social Entrepreneur Ticks: Preparing for Social Entrepreneurship
- 05 Where to Begin? The Social Enterprise Model Canvas
- 06 Developing your Social Enterprise Model Canvas
- 07 Theory of Change and 1-1 SEMC Consultation with raiSE Staff